Your Trusted Partner for Comprehensive Business Process Management
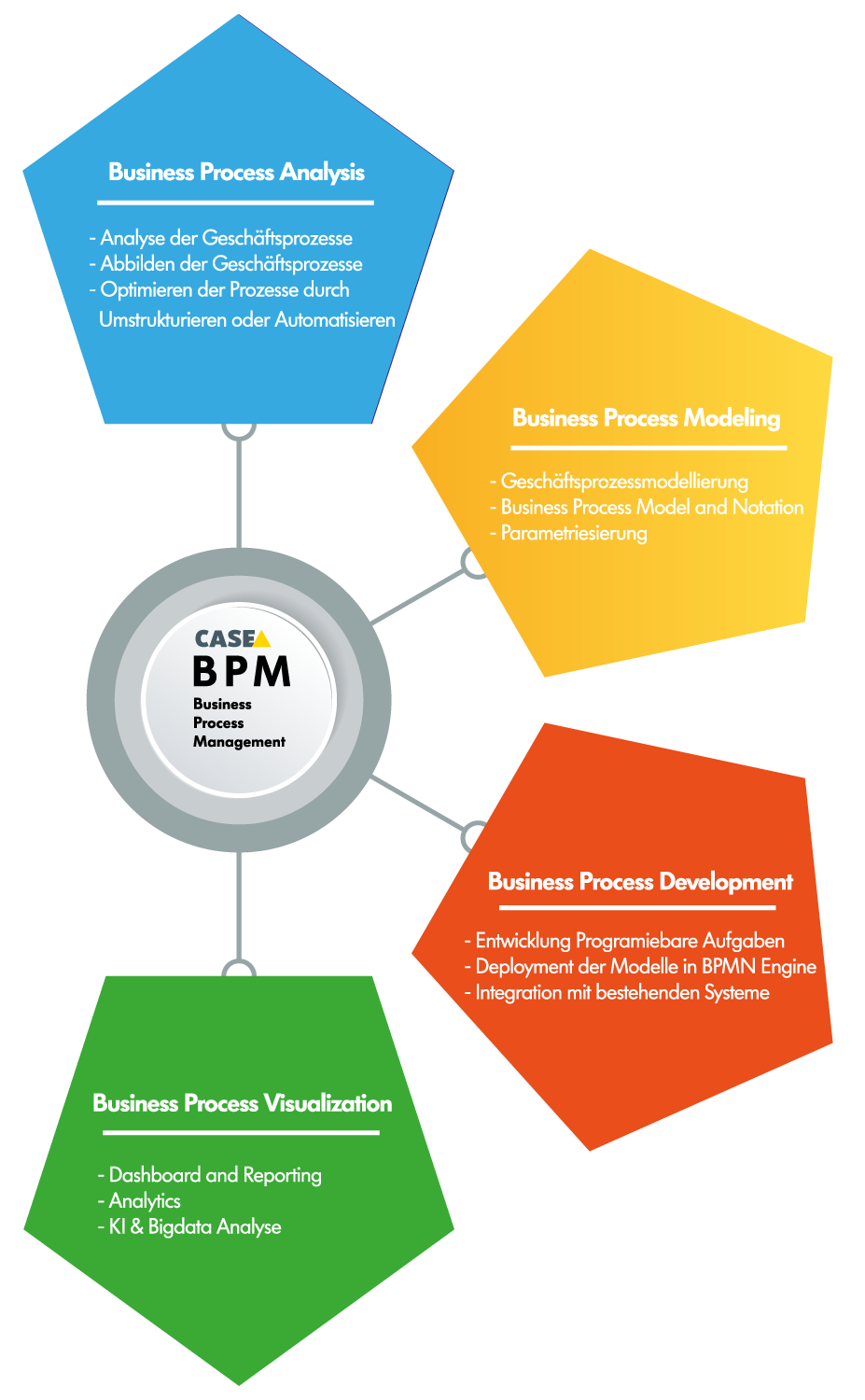
Business Process Management scope
Business process analysis (BPA) is a methodology used by organizations to understand the specific processes that are undertaken to accomplish business objectives. The ultimate goal of BPA is to identify areas of improvement, increase efficiency and effectiveness, and align business processes with business strategy and objectives.
Here are some key points to consider in Business Process Analysis:
- Identifying processes: The first step in BPA is to identify all the processes that are undertaken in the organization. This involves mapping out the workflow in various departments and identifying all the processes involved in achieving the business objectives.
- Analyzing processes: Once the processes have been identified, the next step is to analyze them. This could involve scrutinizing the sequence of tasks, the time taken to complete them, the resources used, the output, etc. It’s crucial to understand how these processes impact the organization’s efficiency, productivity, and bottom-line.
- Benchmarking: Benchmarking involves comparing the organization’s processes with industry standards or best practices. This helps the organization understand where they stand compared to others and identify areas where they could improve.
- Identifying improvements: The main objective of BPA is to identify areas of improvement. Based on the analysis and benchmarking, the organization can pinpoint the processes that are inefficient or ineffective and come up with strategies to improve them.
- Implementing improvements: After identifying the improvements, the next step is to implement them. This could involve changing the way tasks are done, retraining staff, acquiring new technology, etc.
- Monitoring: The final step in BPA is monitoring the processes to ensure that the improvements are having the desired impact. This involves regularly reviewing the processes and making necessary adjustments.
To carry out an effective BPA, organizations often employ business analysts who have the requisite skills and knowledge. They might also use various tools and software that help in process mapping, analysis, and improvement. It’s also important to note that BPA is not a one-time activity. It should be an ongoing effort to continuously improve the processes and enhance the organization’s overall performance.
Business Process Modeling (BPM) is a technique used by businesses to visualize and understand their current business processes. It is often performed by business analysts who aim to get a clear view of the business workflow, interconnections, and dependencies within processes, which can be instrumental in optimizing and automating them.
In the most basic terms, a business process is a set of activities that, when completed, will accomplish an organizational goal. The main benefit of BPM is that it helps to visualize what is happening in an organization, identify potential improvements, and project how they will affect the business’s operation.
Some important aspects of Business Process Modeling include:
1. BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation):
This is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. It provides businesses with a standard notation that is easy to understand for all business stakeholders, including business analysts, technical developers, and business managers.
2. Workflows:
These define the sequence of tasks that make up a business process. The workflow represents the way tasks are grouped, who performs them, and what conditions dictate the sequence of tasks.
3. Process Maps:
These are visual representations of the business process, including the sequence of tasks, the stakeholders involved, and the desired outcomes. They can help identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and other opportunities for process improvement.
4. Business Rules:
These are specific, actionable, testable directives that are under the control of the business and that serve as a constraint against which business behavior can be judged. They are often used to help define parts of a business process.
The ultimate goal of BPM is to increase efficiency, performance, and agility in the day-to-day operations of a business. It can also help to ensure that the business is compliant with all relevant regulations and standards. BPM software (BPMS) is often used to manage and analyze the data produced by business process models.
Our business process development strategy is centered around comprehensive integration with existing systems, including but not limited to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Online Shops, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and other vital tools. We are equipped to deploy models within various Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) Engines such as Flowable, Camunda, Alfresco, and IBM BPM, ensuring that your business processes are optimally designed and executed.
In the current digital era, we prioritize a cloud-oriented, microservices-based approach. This means that each function of your business process runs as an independent service, allowing for flexibility, scalability, and ease of modification.
To further enhance efficiency, we automate tasks through the use of External, Scripted, and Service Tasks. These tools enable us to automate repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and free your employees to focus on more strategic operations.
Furthermore, we specialize in programming custom forms tailored to your specific business needs. This enables your team to collect, analyze, and manage data effectively and efficiently.
Lastly, we are also adept at implementing technology such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and IP PBX systems among others. These systems improve document processing and telecommunication services, further streamlining your business operations and maximizing productivity.
Our business process development solutions are designed to modernize your operations, improve efficiency, and drive your business towards growth and success.
Benefits of CASE Deutschland GmbH Business Process Visualization:
- Clearer Understanding: Visualizing a process can make it easier to understand, particularly for people who are not familiar with the process.
- Improved Communication: It can help to communicate the process to stakeholders, ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Process Improvement: It can highlight inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas of the process that can be improved.
- Documentation: It serves as a reference material for training new employees or for revisiting the process in the future.
- Compliance: It can help to ensure compliance with regulations by providing a clear view of the process.
In the context of business process visualization, these elements can play a crucial role:
1. Reporting:
Reporting in business refers to the communication of results, conditions, or events that have occurred within a company to those with an interest or need in the information. This is often structured, recurrent, and generated through automated processes.
2. Alerting:
Alerting in the business context typically refers to the use of technology to notify relevant personnel about important events or conditions. Alerts can be triggered by a wide range of situations, such as system errors, security breaches, or deviations from key performance indicators (KPIs).
3. Analytics:
Analytics refers to the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. In business, this often involves the use of specialized systems and software to gather and process data from various sources to generate insights that can aid in decision-making.
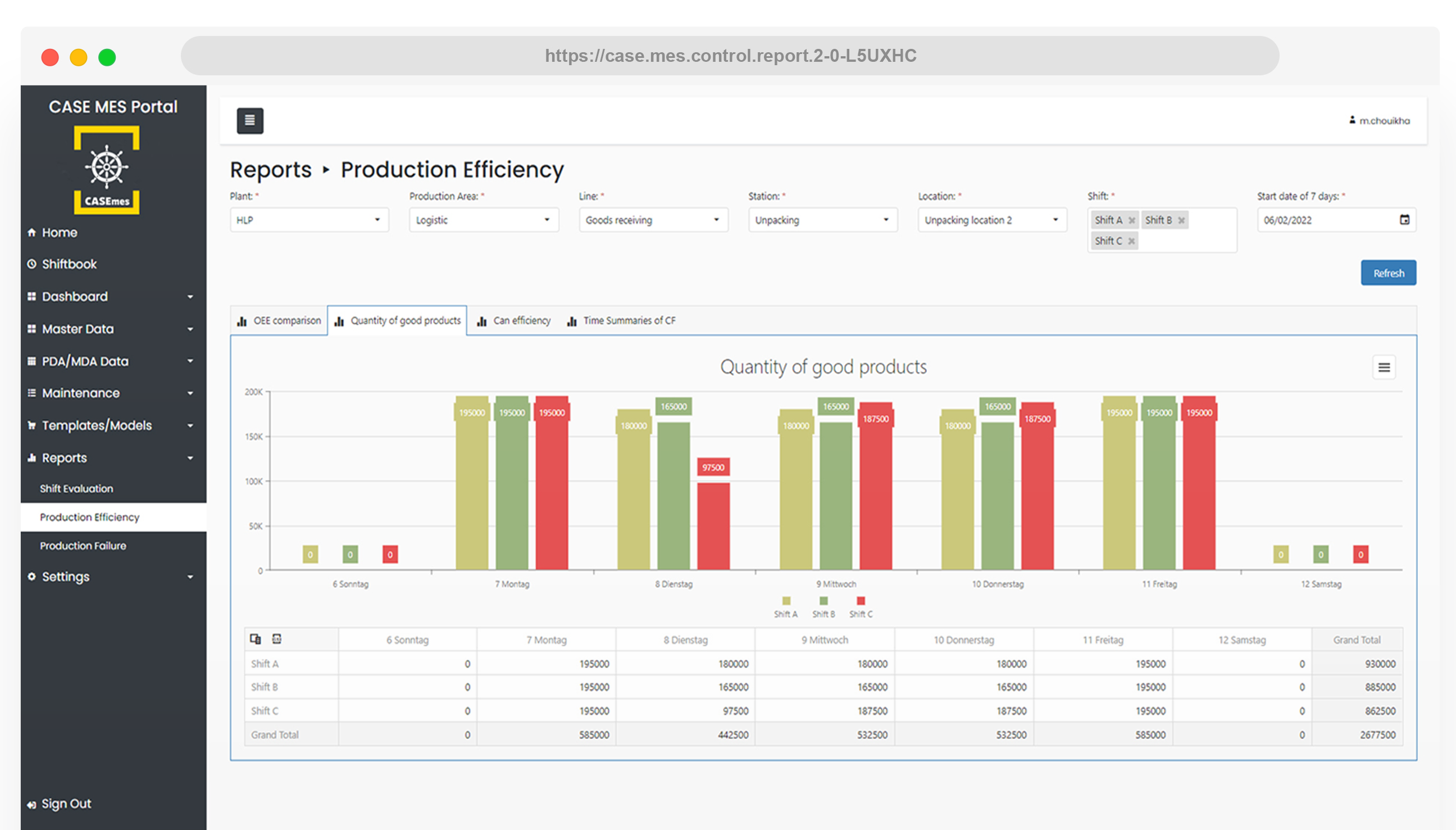
4. Custom Dashboard:
A custom dashboard is a user interface that presents data in a way that is easy to read and interpret, often using charts, graphs, and tables. Dashboards are usually customizable to suit the specific needs and preferences of the user or the organization, allowing them to focus on the most relevant data and KPIs.
5. AI-related Reporting:
This involves the use of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to generate, enhance, or automate reporting processes. This can include everything from using AI to automatically generate written reports based on data, to using machine learning algorithms to predict future trends and present these predictions in reports.
6. AI and Big Data Deployment:
This refers to the implementation of artificial intelligence and big data technologies within an organization. Big data refers to the large volumes of data that businesses collect from various sources, which can be analyzed to reveal patterns, trends, and insights. AI can be used to process and analyze this data more effectively and efficiently than traditional methods. The deployment of these technologies can involve a wide range of activities, such as setting up data storage and processing infrastructure, developing or implementing AI algorithms, and integrating these technologies with existing systems and processes.
In the context of business process visualization, these elements can play a crucial role. For example, reporting and analytics can provide data that helps to understand and optimize business processes. Dashboards can visualize this data in a way that’s easy to understand and act upon. AI can enhance these capabilities, for example by predicting future process outcomes or by automating parts of the process. Finally, alerting can be used to notify relevant personnel when important events occur in a process, such as when a process step takes longer than expected or when a process outcome deviates from a set threshold.
- Business Process Analysis
-
Business process analysis (BPA) is a methodology used by organizations to understand the specific processes that are undertaken to accomplish business objectives. The ultimate goal of BPA is to identify areas of improvement, increase efficiency and effectiveness, and align business processes with business strategy and objectives.
Here are some key points to consider in Business Process Analysis:
- Identifying processes: The first step in BPA is to identify all the processes that are undertaken in the organization. This involves mapping out the workflow in various departments and identifying all the processes involved in achieving the business objectives.
- Analyzing processes: Once the processes have been identified, the next step is to analyze them. This could involve scrutinizing the sequence of tasks, the time taken to complete them, the resources used, the output, etc. It’s crucial to understand how these processes impact the organization’s efficiency, productivity, and bottom-line.
- Benchmarking: Benchmarking involves comparing the organization’s processes with industry standards or best practices. This helps the organization understand where they stand compared to others and identify areas where they could improve.
- Identifying improvements: The main objective of BPA is to identify areas of improvement. Based on the analysis and benchmarking, the organization can pinpoint the processes that are inefficient or ineffective and come up with strategies to improve them.
- Implementing improvements: After identifying the improvements, the next step is to implement them. This could involve changing the way tasks are done, retraining staff, acquiring new technology, etc.
- Monitoring: The final step in BPA is monitoring the processes to ensure that the improvements are having the desired impact. This involves regularly reviewing the processes and making necessary adjustments.
To carry out an effective BPA, organizations often employ business analysts who have the requisite skills and knowledge. They might also use various tools and software that help in process mapping, analysis, and improvement. It’s also important to note that BPA is not a one-time activity. It should be an ongoing effort to continuously improve the processes and enhance the organization’s overall performance.
- Business Process Modeling
-
Business Process Modeling (BPM) is a technique used by businesses to visualize and understand their current business processes. It is often performed by business analysts who aim to get a clear view of the business workflow, interconnections, and dependencies within processes, which can be instrumental in optimizing and automating them.
In the most basic terms, a business process is a set of activities that, when completed, will accomplish an organizational goal. The main benefit of BPM is that it helps to visualize what is happening in an organization, identify potential improvements, and project how they will affect the business’s operation.
Some important aspects of Business Process Modeling include:
1. BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation):
This is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. It provides businesses with a standard notation that is easy to understand for all business stakeholders, including business analysts, technical developers, and business managers.
2. Workflows:
These define the sequence of tasks that make up a business process. The workflow represents the way tasks are grouped, who performs them, and what conditions dictate the sequence of tasks.
3. Process Maps:
These are visual representations of the business process, including the sequence of tasks, the stakeholders involved, and the desired outcomes. They can help identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and other opportunities for process improvement.
4. Business Rules:
These are specific, actionable, testable directives that are under the control of the business and that serve as a constraint against which business behavior can be judged. They are often used to help define parts of a business process.
The ultimate goal of BPM is to increase efficiency, performance, and agility in the day-to-day operations of a business. It can also help to ensure that the business is compliant with all relevant regulations and standards. BPM software (BPMS) is often used to manage and analyze the data produced by business process models.
- Business Process Development
-
Our business process development strategy is centered around comprehensive integration with existing systems, including but not limited to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Online Shops, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and other vital tools. We are equipped to deploy models within various Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) Engines such as Flowable, Camunda, Alfresco, and IBM BPM, ensuring that your business processes are optimally designed and executed.
In the current digital era, we prioritize a cloud-oriented, microservices-based approach. This means that each function of your business process runs as an independent service, allowing for flexibility, scalability, and ease of modification.
To further enhance efficiency, we automate tasks through the use of External, Scripted, and Service Tasks. These tools enable us to automate repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and free your employees to focus on more strategic operations.
Furthermore, we specialize in programming custom forms tailored to your specific business needs. This enables your team to collect, analyze, and manage data effectively and efficiently.
Lastly, we are also adept at implementing technology such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and IP PBX systems among others. These systems improve document processing and telecommunication services, further streamlining your business operations and maximizing productivity.
Our business process development solutions are designed to modernize your operations, improve efficiency, and drive your business towards growth and success.
- Business Process Visualization
-
Benefits of CASE Deutschland GmbH Business Process Visualization:
- Clearer Understanding: Visualizing a process can make it easier to understand, particularly for people who are not familiar with the process.
- Improved Communication: It can help to communicate the process to stakeholders, ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Process Improvement: It can highlight inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas of the process that can be improved.
- Documentation: It serves as a reference material for training new employees or for revisiting the process in the future.
- Compliance: It can help to ensure compliance with regulations by providing a clear view of the process.
In the context of business process visualization, these elements can play a crucial role:
1. Reporting:
Reporting in business refers to the communication of results, conditions, or events that have occurred within a company to those with an interest or need in the information. This is often structured, recurrent, and generated through automated processes.
2. Alerting:
Alerting in the business context typically refers to the use of technology to notify relevant personnel about important events or conditions. Alerts can be triggered by a wide range of situations, such as system errors, security breaches, or deviations from key performance indicators (KPIs).
3. Analytics:
Analytics refers to the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. In business, this often involves the use of specialized systems and software to gather and process data from various sources to generate insights that can aid in decision-making.
4. Custom Dashboard:
A custom dashboard is a user interface that presents data in a way that is easy to read and interpret, often using charts, graphs, and tables. Dashboards are usually customizable to suit the specific needs and preferences of the user or the organization, allowing them to focus on the most relevant data and KPIs.
5. AI-related Reporting:
This involves the use of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to generate, enhance, or automate reporting processes. This can include everything from using AI to automatically generate written reports based on data, to using machine learning algorithms to predict future trends and present these predictions in reports.
6. AI and Big Data Deployment:
This refers to the implementation of artificial intelligence and big data technologies within an organization. Big data refers to the large volumes of data that businesses collect from various sources, which can be analyzed to reveal patterns, trends, and insights. AI can be used to process and analyze this data more effectively and efficiently than traditional methods. The deployment of these technologies can involve a wide range of activities, such as setting up data storage and processing infrastructure, developing or implementing AI algorithms, and integrating these technologies with existing systems and processes.
In the context of business process visualization, these elements can play a crucial role. For example, reporting and analytics can provide data that helps to understand and optimize business processes. Dashboards can visualize this data in a way that’s easy to understand and act upon. AI can enhance these capabilities, for example by predicting future process outcomes or by automating parts of the process. Finally, alerting can be used to notify relevant personnel when important events occur in a process, such as when a process step takes longer than expected or when a process outcome deviates from a set threshold.